Article reviewed for Accuracy by Dr. Asmat Khan.

As cannabis legalization spreads globally, veterinarians are increasingly encountering cases of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) toxicity in pets, particularly dogs. THC, the psychoactive component in cannabis, can cause severe health issues in dogs, including lethargy, disorientation, vomiting, and even seizures. While veterinarians are equipped to manage these medical emergencies, the question of veterinarian-client confidentiality is a critical yet often overlooked aspect of these cases. Pet owners often hesitate to disclose cannabis exposure due to fear of legal repercussions, embarrassment, or stigma, which can hinder effective treatment. This essay explores the concept of veterinarian-client confidentiality and how it applies to cases involving THC toxicity, highlighting its importance for pet welfare and ethical veterinary practice.
Understanding Veterinarian-Client Confidentiality
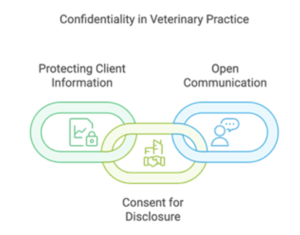
Veterinarian-client confidentiality is the ethical and legal principle that a veterinarian must keep a client’s information private unless consent is given to disclose it. Similar to doctor-patient confidentiality, this principle ensures that clients feel comfortable sharing sensitive information about their pet’s health and environment, enabling accurate diagnoses and effective treatment. While confidentiality laws vary across jurisdictions, the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) and other professional bodies uphold it as a cornerstone of ethical veterinary practice.
Key aspects of confidentiality include:
- Protecting Client Information: Veterinarians must safeguard any personal, medical, or environmental information shared by the client.
- Obtaining Consent for Disclosure: Information can only be shared with third parties if the client provides explicit consent, except in cases required by law.
- Promoting Open Communication: Confidentiality fosters trust between the veterinarian and client, encouraging honest communication about potential health risks.
THC Toxicity in Pets: The Role of Disclosure
Cases of THC toxicity in dogs often arise from accidental ingestion of edibles, cannabis plants, or residues from smoking. Symptoms can include disorientation, ataxia (loss of coordination), vomiting, tremors, and in severe cases, seizures or coma. Effective treatment depends on the veterinarian knowing the cause of the toxicity, as prompt and accurate interventions—such as inducing vomiting, administering activated charcoal, or providing IV fluids—are crucial. Inducing vomiting is typically effective if the ingestion occurred within two hours. However, this approach is avoided if the pet is disoriented or unconscious due to the risk of aspiration.
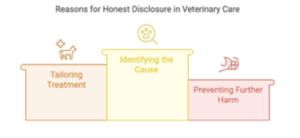
The Importance of Honest Disclosure
- Identifying the Cause: Pet owners must disclose whether their dog may have ingested cannabis for the veterinarian to determine the appropriate course of action. Without this information, delays in diagnosis can worsen the pet’s condition.
- Tailoring Treatment: THC toxicity requires specific interventions that differ from treatments for other toxins, such as chocolate or household chemicals.
- Preventing Further Harm: Honest disclosure enables veterinarians to advise pet owners on how to prevent future incidents, ensuring the pet’s long-term safety.
Challenges to Confidentiality in THC Toxicity Cases
Despite the importance of disclosure, pet owners often reluctant to share information about cannabis exposure due to various concerns:
- Fear of Legal Repercussions: In jurisdictions where cannabis use is restricted or illegal, pet owners may worry about being reported to authorities.
- Social Stigma: Even in areas where cannabis is legal, some clients may fear judgment from veterinary staff or others for perceived negligence.
- Lack of Awareness: Some pet owners may not realize that cannabis can be harmful to pets or that disclosing this information is vital for treatment.
Veterinarians must navigate these challenges while maintaining professional and ethical standards, ensuring the pet receives timely care without compromising client trust.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Legal Obligations
Veterinarian-client confidentiality laws vary by jurisdiction. In some areas, veterinarians are legally required to report cases of animal abuse or neglect, which could include repeated exposure to harmful substances like THC. However, most cases of THC toxicity are accidental and do not meet the threshold for neglect.
To navigate these complexities, veterinarians should:
- Familiarize themselves with local laws regarding confidentiality and mandatory reporting.
- Understand that while disclosure may be required in rare cases of intentional harm, confidentiality can typically be maintained for accidental exposures.
Ethical Responsibilities
Even when not legally mandated, veterinarians have an ethical responsibility to prioritize the pet’s welfare while respecting the client’s confidentiality. Open communication is essential to building trust and ensuring clients feel safe providing necessary information.
Best Practices for Veterinarians in THC Toxicity Cases
To balance ethical and legal considerations while ensuring effective care, veterinarians can adopt the following practices:
Create a Judgment-Free Environment
- Avoid shaming or reprimanding clients for their pet’s exposure to THC. Use compassionate, nonjudgmental language to encourage honesty.
- Example: Instead of saying, “How could you let this happen?” say, “It’s important for me to understand what your dog might have ingested so I can provide the best care.”
Educate Clients
- Provide information about the effects of THC on pets and emphasize the importance of disclosure in emergencies.
- Offer practical advice on safely storing cannabis products to prevent future incidents.
Tip:
- Use brochures, infographics, or follow-up emails to reinforce key points. Visual aids can be particularly helpful in educating clients
-
- Maintain Confidentiality
- Reassure clients that their information will remain private unless disclosure is legally required. This reassurance can reduce fear of judgment or legal consequences, making clients more likely to share critical information..
Document Information Securely
- Record details of the case accurately and securely, ensuring compliance with confidentiality laws and ethical guidelines.
Advocate for Clarity in Reporting Laws
- Work with professional associations to advocate for clear, consistent laws regarding confidentiality and reporting in cases of accidental THC exposure.
Building Trust Through Confidentiality
Veterinarian-client confidentiality is not just a legal requirement; it is a foundation of trust that empowers clients to share vital information. In THC toxicity cases, this trust can mean the difference between effective treatment and delayed care. By fostering open communication and maintaining confidentiality, veterinarians can ensure that pets receive the care they need without compromising client relationships.
Conclusion
As THC toxicity cases become more common, veterinarians must navigate the complex intersection of medical care, legal obligations, and client trust. Veterinarian-client confidentiality plays a crucial role in encouraging honest disclosure, enabling effective treatment, and fostering long-term trust between veterinarians and pet owners. By adhering to ethical guidelines, maintaining a judgment-free approach, and staying informed about local laws, veterinarians can ensure the best outcomes for both pets and their owners in these increasingly relevant cases.