Article reviewed for Accuracy by Dr. Asmat Khan.

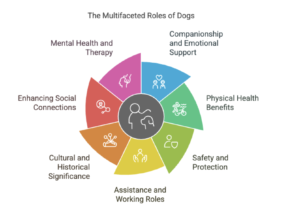
Dogs have been an integral part of human life for thousands of years. Their significance extends beyond companionship, encompassing roles in physical and mental health, security, work, and even cultural and historical contexts. As one of the first domesticated animals, dogs have evolved alongside humans, forming a unique bond that makes them invaluable in various aspects of our lives. This essay explores why dogs are important to humans, highlighting their roles as companions, protectors, helpers, and healers.
Companionship and Emotional Support
Dogs are often referred to as “man’s best friend,” a title that aptly describes their role as loyal companions. Their ability to form strong emotional bonds with humans is unparalleled in the animal kingdom. Dogs provide unconditional love and support, offering comfort during times of stress, sadness, or loneliness. Their presence can reduce feelings of isolation, especially for individuals who live alone or struggle with social connections.
Scientific studies support the idea that owning a dog can have profound psychological benefits. Interacting with dogs can trigger the release of oxytocin, often called the “love hormone,” which fosters feelings of happiness and bonding. Furthermore, dogs can sense human emotions, responding with affection or playful behavior to lift their owners’ spirits. This emotional connection not only improves mental well-being but also fosters a sense of purpose and responsibility in dog owners.
Physical Health Benefits
The companionship of dogs also contributes to better physical health. Dog owners are more likely to engage in regular physical activity, as walking and playing with a dog requires consistent effort. This increased activity helps maintain cardiovascular health, reduces obesity, and improves overall fitness levels.

Additionally, studies have shown that spending time with dogs can lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and decrease stress-related hormones such as cortisol. Dogs can also improve immune system functioning, especially in children exposed to them at a young age. These health benefits highlight the significant role dogs play in enhancing the quality of human life.
Safety and Protection
One of the earliest roles dogs played in human societies was that of a protector. From guarding homes and livestock to serving as watchful companions on dangerous journeys, dogs have consistently been a source of security. Their keen senses, particularly their acute sense of smell and hearing, make them excellent at detecting potential threats.
Even today, dogs serve in various protective roles. Police and military dogs are trained to detect explosives, narcotics, and other hazards, as well as to apprehend suspects. Guard dogs protect homes and businesses, deterring intruders and alerting their owners to danger. For individuals with disabilities or medical conditions, specially trained service dogs can provide life-saving assistance by detecting seizures, retrieving medication, or guiding their owners away from harm.
Assistance and Working Roles
Dogs are invaluable in their capacity to assist humans in a wide range of work environments. Service dogs support individuals with disabilities, including those who are visually impaired, hearing impaired, or physically disabled. Therapy dogs visit hospitals, nursing homes, and schools to provide comfort and emotional support to patients, residents, and students.
In professional settings, working dogs contribute to fields such as search and rescue, agriculture, and law enforcement. Search and rescue dogs are deployed during natural disasters, using their exceptional sense of smell to locate survivors trapped under rubble. Herding dogs assist farmers in managing livestock, ensuring efficiency and safety in agricultural operations. Detection dogs are employed at airports and borders to sniff out illegal substances, ensuring public safety and security.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The importance of dogs extends beyond practical roles; they hold a special place in human culture and history. Dogs have been featured in art, literature, and mythology across various civilizations. Ancient Egyptians revered dogs, associating them with the god Anubis, who was depicted with a canine head. In Chinese culture, the Year of the Dog in the zodiac symbolizes loyalty and honesty. Dogs also played a critical role in exploration and innovation. For instance, sled dogs enabled humans to navigate the Arctic and Antarctic regions, aiding explorers such as Roald Amundsen and Robert Falcon Scott. These historical contributions underscore the enduring partnership between dogs and humans.

Enhancing Human Social Connections
Dogs often act as social catalysts, helping their owners form connections with others. Dog owners frequently interact with fellow pet owners during walks or at dog parks, fostering a sense of community. This social interaction can reduce feelings of isolation and encourage a more active social life. Moreover, dogs are increasingly being used in educational and therapeutic programs to teach empathy, responsibility, and communication skills. For example, children with developmental disorders often benefit from interacting with therapy dogs, which can help improve their social and emotional development.
Mental Health and Therapy
Dogs are widely recognized for their therapeutic effects on mental health. Therapy dogs are used to assist individuals with conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and depression. Their calming presence and nonjudgmental nature create a safe space for individuals to express their emotions and regain a sense of stability.

For veterans and first responders, therapy dogs have proven effective in reducing PTSD symptoms, including nightmares, flashbacks, and hypervigilance. Similarly, individuals in rehabilitation programs often find motivation and encouragement through interactions with therapy dogs.
Conclusion
The importance of dogs to humans cannot be overstated. As companions, protectors, helpers, and healers, they enrich our lives in countless ways. Their ability to provide emotional support, improve physical health, and enhance safety and security makes them indispensable members of society. Furthermore, their roles in cultural and historical contexts highlight the deep-rooted connection between dogs and humans.
By understanding and appreciating the multifaceted contributions of dogs, we can ensure that this unique bond continues to thrive. In return for their unwavering loyalty and service, humans have a responsibility to provide dogs with love, care, and respect, fostering a partnership that benefits both species for generations to come.